Hip Fractures: Extracapsular Neck of Femur Fractures
Definition of an extracapsular neck of femur fracture (#NOF)
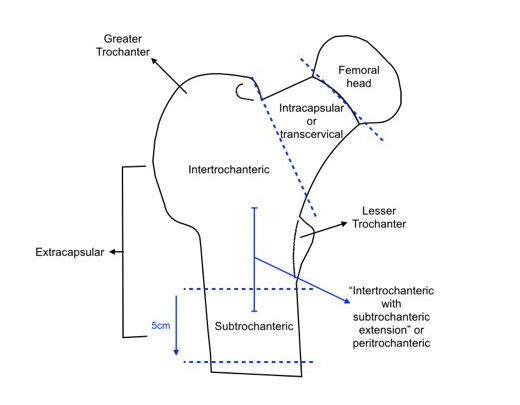
- Extra capsular neck of femur fractures (#NOF) are fractures of the neck of the femur which occur outside the capsule of the hip joint. As such the risks of avascular necrosis of the femoral head or no longer a concern
- These can be described as intertrochanteric (i.e. along a line that connects the lesser and greater trochanters of the femur) or subtrochanteric (below the level of the lesser trochanter) – see pictures below
- A fracture must be no more than 5cm below the lesser trochanter, otherwise it is treated as a femoral shaft fracture
Epidemiology of extracapsular neck of femur fractures
- Much like intracapsular fractures, these are most commonly a fracture of elderly, osteoporotic bone
- As an entity (both intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric) extracapsular neck of femur fractures are almost twice as common as intracapsular fractures
Risk factors for extracapsular neck of femur fractures
- Once again the cause is predominantly a direct trauma from a fall onto the affected hemipelvis
- Risk factors are similar to intracapsular fractures. They are more common in those with moderate to severe hip osteoarthritis, as this renders the intertrochanteric region an area of greater stress. This might account for their greater prevalence in what is a largely elderly age group
Presentation of extracapsular neck of femur fractures
- Pain in the groin radiating down to the thigh
- Inability to weight bear
- Reduced hip range of movement
- The affected limb is often shortened (but less likely externally rotated)
- There is often bruising around the joint as any bone haematoma is not contained within the joint capsule (i.e. a haematoma versus a haemarthrosis in intracapsular fractures).
Differential diagnosis of extracapsular neck of femur fractures
- Intracapsular neck of femur fractures or femoral shaft fractures
- Severe osteoarthritis of the hip/fracture osteophytes
- Acetabular/pelvic fractures (including pubic symphysis fractures)
- Septic arthritis of the hip
- Radicular pain from spinal pathology
- Psoas abscess
Describing types of extracapsular neck of femur fractures
- Describe the fracture in terms of:
- 1. Intertrochanteric or subtrochanteric
- 2. Displacement and overall stability
- 3. Involvement of the trochanters themselves
- 4. Degree of shortening and degree of subtrochanteric extension where present
Initial management of extracapsular neck of femur fractures
- ABC approach
- Bloods including G&S and coagulation
- Fluids +/- RBC if shocked
- ECG (pre-op)
- Po analgesia +/- a fascia iliaca block once confirmed
- AP and lateral radiographs of the pelvis and affected hip +/- full length femur radiographs if there is any suggestion of pathological fracture (e.g. malignancy)
- Discuss with the orthopaedic on call team
Further management of extracapsular neck of femur fractures (depends on type)
- Intertrochanteric fractures
- Usually a sliding or dynamic hip screw (DHS) and plate system following closed reduction on a traction table in theatre
- Sub trochanteric or 4-part intertrochanteric fractures
- Due to the inherent instability associated with these fracture, the above procedure (DHS) is likely to result in failure of metalwork or superior cutting out of the screw.
- As such, these fractures are commonly managed with a intramedullary (I.M) nail allowing force distribution at the centre of the fracture line and also some degree of load sharing
Complications of extracapsular neck of femur fractures
- Blood loss in theatre
- Venous thromboembolic disease
- Fat emboli (more common in intramedullary fixation with reamed devices)
- Avascular necrosis (rare)
- Mal-union or non-union of the fracture
- Infection of metalwork
Prognosis of extracapsular neck of femur fractures
- The presence of a hip fracture increase mortality for the first year
- After this period and levels return back to near normal
Click here for medical student OSCE and PACES questions about Hip Fractures: Extracapsular Neck of Femur Fractures
Common Hip Fractures: Extracapsular Neck of Femur Fractures exam questions for medical students, finals, OSCEs and MRCP PACES
Click here to download free teaching notes on Hip Fractures: Extracapsular Neck of Femur Fractures
Perfect revision for medical students, finals, OSCEs and MRCP PACES